Explore Digest
Communication

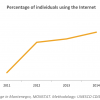
20 ACCESS AND INTERNET USE: 14.1% (2011)
In 2011, only 14.1% of the national population used the Internet in Ghana. When compared to the regional average for all of Sub-Saharan Africa (48 countries), 12.56%, Ghana’s results are slightly above this regional average. Promoting the use of ICTs in all sectors is an objective of the...
20 ACCESS AND INTERNET USE: 14.1% (2011)
In 2011, only 14.1% of the national population used the Internet in Ghana. When compared to the regional average for all of Sub-Saharan Africa (48 countries), 12.56%, Ghana’s results are slightly above this regional average. Promoting the use of ICTs in all sectors is an objective of the Ghana Shared Growth and Development Agenda (2010–2013). In 2008, only 4.3% of the population used the Internet, indicating a substantial increase in just 3 years time.
Digital technologies, in particular the Internet, play a key role in boosting the economy and encouraging new forms of access, creation, production, and the dissemination of ideas, information and cultural content. Though growing, Ghana’s result remains rather low and may reflect the need to increase investments in the development of infrastructures, policies and measures that facilitate the use of new technologies in order to further boost the growth of access and use of ICTs. The country may need to address issues such as pricing, bandwidth, skills, public facilities, content and applications targeting low-end users in order to bring more people online.

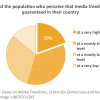
19 FREEDOM OF EXPRESSION: 72/100 (2012)
The freedom of expression is firmly anchored in the Constitution of the Republic of Ghana, which has an entire chapter dedicated to the independence and freedom of the media (Chapter XII).
Ghana’s score of 72/100 indicates that their print, broadcast, and internet-based media...
19 FREEDOM OF EXPRESSION: 72/100 (2012)
The freedom of expression is firmly anchored in the Constitution of the Republic of Ghana, which has an entire chapter dedicated to the independence and freedom of the media (Chapter XII).
Ghana’s score of 72/100 indicates that their print, broadcast, and internet-based media is currently ‘free’, falling just above the benchmark of ‘free’ media. This score illustrates the efforts made to support an enabling environment in Ghana for free media to operate and in which freedom of expression is respected and promoted. Such an environment is a condition for fostering the free flow of ideas, knowledge, information and content, for building knowledge societies, and enhancing creativity, innovation and cultural diversity.
In addition to the rights and freedoms secured in the Constitution, other landmark achievements undertaken by the civil society have also contributed to the advancement of media freedoms. For example, the work of advocacy groups like Media Foundation for West Africa have helped to engender an enabling environment for the flourishing of the freedom of speech and a pluralist media regime.
An additional subjective indicator similarly reveals that a majority of 78% of Ghanaians agreed that they are free to say what they think (79% of men and 77% of women), thus reinforcing the assessment that Ghanaians enjoy the freedom of expression.

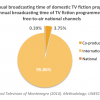
21 DIVERSITY OF FICTIONAL CONTENT ON PUBLIC TELEVISION: 24.7% (2013)
In Ghana, approximately 24.7% of the broadcasting time for television fiction programmes on public free-to-air television is dedicated to domestic fiction programmes. During the observed period, 87% of all fictional content was aired in the national language-...
21 DIVERSITY OF FICTIONAL CONTENT ON PUBLIC TELEVISION: 24.7% (2013)
In Ghana, approximately 24.7% of the broadcasting time for television fiction programmes on public free-to-air television is dedicated to domestic fiction programmes. During the observed period, 87% of all fictional content was aired in the national language- English; no programmes were aired in any of the 11 government supported local or regional languages.
In contrast, the 2004 Cultural Policy aims for 70% of programmes on national television to be of Ghanaian origin and that “television shall be used to project Ghanaian arts, culture and value systems; enhance national consciousness and self-reliance by making its programme content from indigenous resources, [and] making its programme content relevant to Ghanaian realities, history and aspirations” (Chapter VII). Public broadcasting has major implications for the development of the domestic audio-visual industry, as well as for the flourishing of local cultural expressions and creative products.
Results that do not meet the nationally defined objectives may reflect that in spite of the aspirations of the culture sector, low levels of public support for the dissemination of domestic content (including co-productions) produced by local creators and cultural industries may persist. Cross-analysis with the indicators of the Governance, Education and Economy dimensions reveal that though sectoral laws for film and television are in place, there are only limited opportunities to conduct studies in the field of film and image, as well as limited formal employment. Enhancing the effective implementation of existing policies could further facilitate the sector by increasing education opportunities, encouraging co-productions and increasing levels of public support to stimulate local production and the distribution of creative content.
Gender-Equality

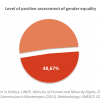
18 PERCEPTION OF GENDER EQUALITY: 45.7% (2007)
In 2007, 45.7% of Ghanaians positively perceived gender as a factor for development, according to their responses to questions regarding three key domains that parallel the objective indicator for this dimension- employment, political participation and education. The final result is a...
18 PERCEPTION OF GENDER EQUALITY: 45.7% (2007)
In 2007, 45.7% of Ghanaians positively perceived gender as a factor for development, according to their responses to questions regarding three key domains that parallel the objective indicator for this dimension- employment, political participation and education. The final result is a composite indicator, which suggests that slightly more than half of the population of Ghana continue to view gender as irrelevant or a negative factor for development. Individuals’ perceptions on gender equality are strongly influenced by cultural practices and norms, thus Ghana’s result suggests that gender-biased social and cultural norms remain dominant.
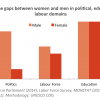
However, the perception of gender equality greatly varied according to the domain of the question asked. When asked if “When jobs are scarce, men should have more right to a job than women,” only 37.4% of respondents did not agree. This means that 62.6% of the population agrees that men have priority in regards to employment. This figure is surprisingly high in comparison to the marginal gap recorded for labour force participation rates between males and females. Unsurprisingly, the most unfavourable perceptions were recorded in regards to political participation. When asked if “Men make better political leaders than women,” only 21.7% of the population responded no. Thus, nearly four-fifths of the population agrees that men are better political leaders. The most favourable perceptions were recorded regarding education. When asked if “University is more important for a boy than for a girl,” 78.1% of respondents did not agree, suggesting that education is a domain in which gender equality is likely to be perceived as a positive factor for development. While the relatively high figure regarding the poor perception of women’s role in political participation correlates with the objective outputs observed, the latter figure on education is inconsistent with the still significant gap regarding men and women’s education.
>> This cross-analysis of the subjective and objective indicators reveals low results overall, both regarding objective outputs and perceptions, as well as inconsistencies in regards to the population’s relatively positive attitudes and values concerning education and the ongoing gaps in actual years of education for men and women. These results suggest a need for both greater advocacy efforts targeting attitudes, as well as improved policies and mechanisms to proactively address key issues such as political participation and education. Since cultural values and attitudes strongly shape perceptions towards gender equality, it is critical to prove that gender equality can compliment and be compatible with cultural values and attitudes, and be an influential factor in the retransmission of cultural values for building inclusive and egalitarian societies, and for the respect of human rights.
Heritage

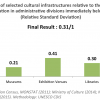
22 HERITAGE SUSTAINABILITY: 0.53/1 (2013)
Article 39.4 of the 1992 Constitution of the Republic of Ghana declares, “the State shall endeavour to preserve and protect places of historical interest and artifacts.” The 2004 Cultural Policy goes further to proclaim, “through State and private initiative, Ghana shall...
22 HERITAGE SUSTAINABILITY: 0.53/1 (2013)
Article 39.4 of the 1992 Constitution of the Republic of Ghana declares, “the State shall endeavour to preserve and protect places of historical interest and artifacts.” The 2004 Cultural Policy goes further to proclaim, “through State and private initiative, Ghana shall develop its heritage and cultural assets and promote their use and appreciation.” Within this context, Ghana’s result of 0.53/1 is an intermediate result regarding the establishment of a multidimensional framework for the protection, safeguarding and promotion of heritage sustainability. The degree of commitment and action taken by Ghanaian authorities is mixed and varies according to the component of the framework. While many public efforts have been dedicated to raising-awareness and creating a national registry for tangible heritage, persisting gaps call for additional actions to improve the framework regarding the updating of registries, the inventorying of elements of intangible heritage, mechanisms for community involvement, and stimulating support amongst the private sector.
Ghana scored 0.26/1 for registration and inscriptions, indicating that while efforts have resulted in national and international registrations of Ghanaian sites of tangible heritage and protected cultural property, increased focus should be placed on updating national registries and expanding recognition to intangible cultural heritage. While Ghana has a national registry for tangible heritage and an inventory of protected cultural property, no database of stolen cultural objects or inventory of intangible heritage yet exists, and existing registries have not been updated since 1999.
Ghana scored 0.59/1 for the protection, safeguarding and management of heritage, indicating that there are several policies and measures in place to prevent illicit-trafficking, regulate archeological excavations and prepare for disaster management, but that no recent concrete policies or measures have been adopted for protecting tangible or intangible heritage, or to involve communities in the processes of identification, registration or inventorying. Though actions taken to prevent illicit-trafficking, such as the delivery of certificates for export, are to be applauded as Ghana has yet to ratify the 1970 UNESCO Convention or the 1995 UNIDROIT Convention, there continues to be no specialized police unit to enforce the prevention of illicit-trafficking of cultural objects or efforts to involve communities in these actions. Other gaps include the publication of regularly updated management plans for major heritage sites and the inclusion of heritage in national development plans.
Ghana scored 0.73/1 for the transmission and mobilization of support, which reflects the recent efforts taken to raise awareness of heritage’s value and its threats amongst the population. In addition to signage at heritage sites and differential pricing, awareness-raising measures have included workshops for teachers and school programmes, as well as media campaigns led by the Ghana Museums and Monuments Board. While much has been done to educate the public, little has been done to gain the support of the civil society and private sector. Additional efforts to involve the civil society in heritage protection, conservation, and transmission, as well as explicit agreements with tour operators are two means to be further explored.
Communication


Economy
Education


Gender-Equality
17GENDER EQUALITY OBJECTIVE OUTPUTS (ALTERNATIVE INDICATORS)
The Law on Gender Equality (2007) has been a significant milestone to create a protective framework against discrimination and in promotion of gender equality in Montenegro. This framework has been further enhanced by the Law on Prohibition of Discrimination (2010), as well...17GENDER EQUALITY OBJECTIVE OUTPUTS (ALTERNATIVE INDICATORS)
Governance
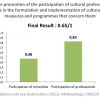
The National Council for Culture provides key opportunities for the participation of cultural professionals in decision-making at the national level. According to the Law on Culture (2008), members of the National Council are appointed by the Government, from the ranks of artists and experts in culture with high reputation, originating from Montenegro and abroad. The National Council for Culture is permanent (mandate for 4 years) and can be considered active, meeting at least once every year. The Council can submit its views, opinions and suggestions to the Government of Montenegro, which remain consultative. At the local level, the Law on Culture prescribes the appointment of Municipal Councils for Culture, whose members should be affirmed artists or experts in culture. However, in this regard, the law is not implemented to the full extent, and so far only 4 of the 23 municipalities in Montenegro have established such a council. In addition to the above, it should be noted that the participation of civil society in decision making processes more generally is defined through the Decree on the Procedure for Cooperation Between State Authorities and Non-governmental Organizations (2011) and the Decree on the Procedure and Manner of Conducting Public Hearings in the Preparation of Laws (2012).


Heritage

Economy
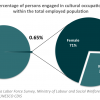
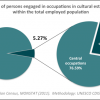
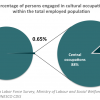
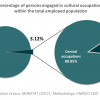
2 CULTURAL EMPLOYMENT: 0.65% (2008)
In 2008, 0.65% of the employed population in Namibia had cultural occupations (4447 people: 29% male and 71% female). 88% of these individuals held occupations in central cultural activities, while 12% held occupations in supporting or equipment related activities.
While already significant,...
2 CULTURAL EMPLOYMENT: 0.65% (2008)
In 2008, 0.65% of the employed population in Namibia had cultural occupations (4447 people: 29% male and 71% female). 88% of these individuals held occupations in central cultural activities, while 12% held occupations in supporting or equipment related activities.
While already significant, the global contribution of the culture sector to employment is underestimated in this indicator due to the difficulty of obtaining and correlating all the relevant data. This figure is only the tip of the iceberg since it does not cover non-cultural occupations performed in cultural establishments or induced occupations with a strong link to culture, such as employees of hospitality services located in or close to heritage sites. In addition, this does not account for employment in the informal culture sector, which is likely to be significant in Namibia. Furthermore, because the raw data in Namibia is only available to the three-digit level of international standard classifications, certain central cultural occupations are not taken into account.
Regardless, this figure highlights low levels of formal cultural employment in Namibia, suggesting that levels of domestic cultural production in the formal sector are also rather low. The relevance of the priorities set aside in the 2001 Policy on Arts and Culture and the former National Development Plan 3 (2007-2012), oriented to increase production and optimize the economic contribution of the culture sector, is thus underlined.
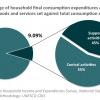
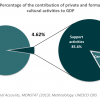
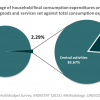
3 HOUSEHOLD EXPENDITURES ON CULTURE: 9.09% (2009/2010)
In Namibia, 9% of household consumption expenditures were devoted to cultural activities, goods and services in the year of 2009/2010 (1400.26 NAD). It is likely that this final result is an over-estimation of the actual percentage of household consumption expenditures spent on...
3 HOUSEHOLD EXPENDITURES ON CULTURE: 9.09% (2009/2010)
In Namibia, 9% of household consumption expenditures were devoted to cultural activities, goods and services in the year of 2009/2010 (1400.26 NAD). It is likely that this final result is an over-estimation of the actual percentage of household consumption expenditures spent on culture due to the current limitations of national data systems which are not exhaustive but rather based on sample groups. As Namibia remains a country of significant divides, often the most isolated groups of the population are not accurately reflected in such data sets due to inaccessibility. The average across all test phase countries of the CDIS is 2.43%, which also suggests that Namibian figures may be overestimated.
Despite the underlined methodological challenges, the national result obtained suggests that there is a real and significant demand from Namibian households for the consumption of foreign and domestic cultural goods, services and activities, and of this 55% is spent on central cultural goods and services, 45% being left to supporting activities and equipment. On average nation-wide, in the category of central cultural goods and services, the most was spent on daily and weekly newspapers (139.45 NAD), watches and personal jewelry (156.90 NAD), and subscription television (292.16 NAD). In the category of support and equipment, a significant share was spent on television sets, decoders, DVD players, and video players (169.95 NAD); and personal computers and laptops (213.16 NAD).
The share of consumption expenditures varies greatly from one region to another in Namibia, from 12.7% and 12.6% in Otjozondzupa and Khomas to 5.9% and 4.2% in Ohangwena and Omusati.
>> While the Economy indicators suggest that there is a significant potential demand for the consumption of cultural goods, services and activities, they also suggest that there is a low level of domestic production in the formal sector, illustrated by the low levels of employment. This is reinforced when cross-analyzing the dimension with other CDIS indicators such as the Diversity of Fictional Content on Public TV, which also suggests low levels of domestic content supply in public broadcasting. High demand and low domestic production would indicate that the full economic potential of the culture sector in Namibia is not being realized.
Education

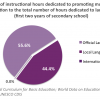
Article 19 of the Constitution of the Republic of Namibia states that “every person is entitled to enjoy, practice, profess, maintain and promote any culture, language, tradition or religion” so long as it does not impinge upon the rights of others. Furthermore, the 2001 Policy on Arts and...
Article 19 of the Constitution of the Republic of Namibia states that “every person is entitled to enjoy, practice, profess, maintain and promote any culture, language, tradition or religion” so long as it does not impinge upon the rights of others. Furthermore, the 2001 Policy on Arts and Culture states that the government has the mission and goal to uphold unity in diversity so that all Namibians feel free to practice any culture, recognizing that such “unity is maintained by mutual understanding, respect and tolerance.” As part of promoting this unity in diversity, the 2001 Policy also states that it is the goal of the Namibian government to safeguard and promote linguistic heritage and acknowledges the role of education in the promotion of cultural diversity. Though not reiterated in the National Development Plan 4 (2013-2017), the National Development Plan 3 (2007-2012) recognized that “language is an essential carrier of culture” and that the biggest challenge post-independence was to heal the wounds of inequality and racism and recognize the wealth of Namibia’s multiculturalism.
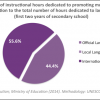
According to the national curriculum for education, updated in 2010, 55.6% of the hours to be dedicated to languages in the first two years of secondary school is to be dedicated to the teaching of the official national language- English. The remaining 44.4% of the time is to be dedicated to the teaching of local and regional languages. Although, the fact that 0% of the required national curriculum is dedicated to additional international languages, such as French or German, these results still indicate that the national curriculum is designed to promote linguistic diversity in Namibia, particularly regarding the promotion of local languages and mother tongues. It should be noted that learners have the option of taking additional international languages such as French or German as one of the prevocational subjects of their choosing.
However, in spite of the promotion of diversity, of the 11 nationally recognized local and regional languages, only 9 are taught in schools. Otjizemba and Ju!hoansi are the only remaining nationally recognized local languages that are not promoted in the education system.

6 ARTS EDUCATION: 2.4% (2010)
The 2001 Policy on Arts and Culture’s stance on “unity in diversity” recognizes that Namibians see themselves as a united nation celebrating the diversity of their artistic and cultural expressions and declares as a goal that the status of the arts should be improved through education and...
6 ARTS EDUCATION: 2.4% (2010)
The 2001 Policy on Arts and Culture’s stance on “unity in diversity” recognizes that Namibians see themselves as a united nation celebrating the diversity of their artistic and cultural expressions and declares as a goal that the status of the arts should be improved through education and that arts subjects should therefore be part of the new curriculum. The policy goes on to state that in such an environment “learners are sure to acquire many skills and self-confidence through exploring their own creative abilities” and that it is “necessary to reverse an alarming trend for the downgrading of the arts and culture.” National Development Plan 3 (2007-2012) also recognized that arts education was necessary for the realization of the country’s creative potential and that a priority should be to “establish a solid foundation of education in the arts and culture.”
Contrasting with the policy statements, the results for this indicator reflect a rather low level of promotion of arts education. According to the updated curriculum of 2010, only 2.4% of the total number of instructional hours is to be dedicated to arts education in the two first years of secondary school (covered by one subject entitled ‘Arts-in-culture’). It should be noted, however, that in addition to the required hours to be dedicated to the arts, learners have the option of taking one additional course entitled ‘Visual and integrated performing arts’ as one of the prevocational courses of their choosing. Nevertheless, this result indicates that instructional hours dedicated to arts education in secondary school remains low, especially when taking into account the average across all test phase countries of the CDIS, which is around 4.84%.
Furthermore, a gap in the offerings of arts education over the course of the educational lifetime emerges. On average, 6.2% of all educational hours are to be dedicated to arts education in primary education. This is nearly three times what is required during secondary education. Moreover, when looking at the following indicator on tertiary and training programmes that are offered in Namibia in the field of culture, it can be noted that the coverage is fairly complete. This gap in arts education during secondary schooling may obstruct both students’ interest in developing a professional career in the culture sector and also concrete opportunities in accessing existing specialized programmes.

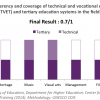
7 PROFESSIONAL TRAINING IN THE CULTURE SECTOR: 0.7/1 (2012)
In the 2001 Policy on Arts and Culture, a key goal was defined to improve the status of the artist “through education and training, and by exploring the economic potential” of the culture sector. The essential link between education, training and employment was made....
7 PROFESSIONAL TRAINING IN THE CULTURE SECTOR: 0.7/1 (2012)
In the 2001 Policy on Arts and Culture, a key goal was defined to improve the status of the artist “through education and training, and by exploring the economic potential” of the culture sector. The essential link between education, training and employment was made. Namibia’s result of 0.7/1 indicates that though complete coverage of cultural fields in technical and tertiary education does not exist in the country, the national authorities have manifested an interest and willingness to invest in the training of cultural professionals. Indeed, the coverage of national public and government-dependent private technical and tertiary education is rather comprehensive in Namibia, offering various types of courses and permitting cultural professionals to receive the necessary education to pursue a career in the culture sector.
Tertiary education is offered by the University of Namibia in the fields of heritage, music, visual and applied arts, and film and image. The College of the Arts also offers technical training in the fields of music, visual and applied arts, and film and image. In addition, the Namibian Training Authority offers one training program in garment making, which falls under the category of visual and applied arts. Although this collection of offerings is fairly inclusive, it is not complete. For instance, no regular technical training programmes exist in the field of heritage, and no technical or tertiary education programmes exist in the field of cultural management, a key area for fostering the emergence of domestic cultural enterprises and industries.
Governance

8 STANDARD-SETTING FRAMEWORK FOR CULTURE: 0.70/1 (2013)
Namibia’s result of 0.70/1 indicates that the country is on the right track and has made many efforts to ratify key international legal instruments affecting cultural development, cultural rights and cultural diversity, as well as to establish a national framework to recognize...
8 STANDARD-SETTING FRAMEWORK FOR CULTURE: 0.70/1 (2013)
Namibia’s result of 0.70/1 indicates that the country is on the right track and has made many efforts to ratify key international legal instruments affecting cultural development, cultural rights and cultural diversity, as well as to establish a national framework to recognize and implement these obligations.
Namibia scored 0.59/1 at the international level, which shows movement in the right direction. Namibia has ratified several important conventions such as the 1972 Convention concerning the Protection of World Cultural and Natural Heritage, the 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage and the 2005 Convention of the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions, all of which are particularly important to the Namibian cultural context. Namibia is still working towards the ratification of certain key international instruments for the protection of cultural assets, such as the 1970 Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Property, the 1995 UNIDROIT Convention on Stolen or Illegally Exported Cultural Objects, and the 1954 Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict.
At the national level, a score of 0.75/1 indicates that national efforts have been made to implement many of the international obligations that Namibia has agreed to at the country level. However, similar to the international level, room for improvement still remains as several key items continue to be missing from the national legislation and regulatory frameworks. For example, no ‘framework law’ for culture exists, and although a sectoral law exists for television and radio, no such laws exist for other sub-sectors such as heritage, books, cinema or music. In the same vein, the lack of regulations dealing with the tax status of culture, such as tax exemptions and incentives designed to benefit the culture sector specifically, also reveals some deficiencies in the establishment of a coherent normative system for supporting the emergence of viable domestic cultural industries that could respond to the proven demand.

CDIS Methodology was developed thanks to the financial support of
Government of Spain
Contact us
UNESCO
Section for the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (CLT/CRE/DCE)
7 place Fontenoy, 75352 Paris 07 SP - France
email: cdis@unesco.org