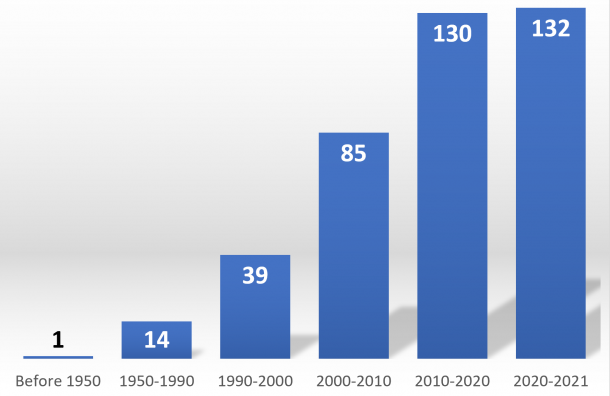
Adoption of ATI laws
Access to Information laws
Progress has been recorded in terms of binding laws and policies giving individuals a right to access information held by public authorities. As of August 2021, 132 UN Member States have adopted constitutional, statutory and/or policy guarantees for public access to information, with at least 22 countries adopting such guarantees since the 2030 Agenda in 2015.[1] In 2021, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia joined the list.[2]
UN Member States that have adopted constitutional, statutory and/or policy guarantees for public access to information (grouped based on the execution of regional activities by UNESCO)
| Europe and North America (50) | Latin America and the Caribbean (25) | Asia and the Pacific (27) | Africa (22) | Arab States (8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | Antigua and Barbuda | Afghanistan | Angola | Jordan |
| Armenia | Argentina | Australia | Benin | Kuwait |
| Austria | Bahamas | Bangladesh | Burkina Faso | Lebanon |
| Azerbaijan | Belize | China | Côte d'Ivoire | Morocco |
| Belarus | Bolivia (Plurinational State of) | Cook Islands | Ethiopia | Saudi Arabia |
| Belgium | Brazil | Fiji | Ghana | Sudan |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Chile | India | Guinea | Tunisia |
| Bulgaria | Colombia | Indonesia | Kenya | Yemen |
| Canada | Costa Rica | Iran (Islamic Republic of) | Liberia | |
| Croatia | Dominican Republic | Japan | Malawi | |
| Cyprus | Ecuador | Kazakhstan | Mozambique | |
| Czechia | El Salvador | Kyrgyzstan | Niger | |
| Denmark | Guatemala | Maldives | Nigeria | |
| Estonia | Guyana | Mongolia | Rwanda | |
| Finland | Honduras | Nepal | Seychelles | |
| France | Jamaica | New Zealand | Sierra Leone | |
| Georgia | Mexico | Pakistan | South Africa | |
| Germany | Nicaragua | Palau | South Sudan | |
| Greece | Panama | Philippines | Uganda | |
| Hungary | Paraguay | Republic of Korea | United Republic of Tanzania | |
| Iceland | Peru | Sri Lanka | Zimbabwe | |
| Ireland | Saint Kitts and Nevis | Tajikistan | ||
| Israel[3] | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Thailand | ||
| Italy | Trinidad and Tobago | Timor-Leste | ||
| Latvia | Uruguay | Uzbekistan | ||
| Liechtenstein[4] | Vanuatu | |||
| Lithuania | Viet Nam | |||
| Luxembourg | ||||
| Malta | ||||
| Monaco | ||||
| Montenegro | ||||
| Netherlands | ||||
| North Macedonia | ||||
| Norway | ||||
| Poland | ||||
| Portugal | ||||
| Republic of Moldova | ||||
| Romania | ||||
| Russian Federation | ||||
| San Marino | ||||
| Serbia | ||||
| Slovakia | ||||
| Slovenia | ||||
| Spain | ||||
| Sweden | ||||
| Switzerland | ||||
| Turkey | ||||
| Ukraine | ||||
| United Kingdom of Great Britain & Northern Ireland | ||||
| United States of America[5] |
Respondents to UNESCO Survey on Public Access to Information
In 2021, UNESCO invited all UN Member States, including associated territories, to participate in a survey based upon on SDG Indicator 16.10.2. The survey took place between April and June 2021. As many as 102 countries, including territories, responded to the survey.[6]

[1] Argentina, Bahamas, Costa Rica, Cyprus, Fiji, Ghana, Kenya, Kuwait, Lebanon, Luxembourg, Malawi, Morocco, Vanuatu, Philippines, Timor-Leste, Saudi Arabia, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, Viet Nam, Togo, United Republic of Tanzania.
[2] Gambia also passed the Access to Information Bill in July 2021, yet as of the writing of this report in August 2021, the Bill has yet to be included in the official gazette, hence it has not yet included in the list.
[3] Israel withdrew from UNESCO on 31 December 2018.
[4] Lichtenstein is not a member of UNESCO.
[5] United States of America withdrew from UNESCO on 31 December 2018.
[6] The four territories participating in the survey were Gibraltar, Isle of Man, Jersey and Cayman Islands. Gibraltar and Cayman Islands are non-self-governing territories administrated by the United Kingdom; The Isle of Man and Jersey are internally self-governing dependencies of the British Crown, United Kingdom.


